Geneall.cambio.co.uk
DNA PURIFICATION HANDBOOK
AmpONETM, DirExTM, ExfectionTM, ExgeneTM, ExpinTM, ExprepTM, EzClearTM, EzSepTM,
GenExTM,
Hybrid-QTM, RiboExTM, RiboclearTM, RibospinTM are trademarks of GeneAll Biotechnology co., ltd.
2013 GeneAll Biotechnology, all right reserved.
This protocol handbook is included in :
GeneAll® ExprepTM Plasmid SV mini (101-150, 101-102, 101-111)GeneAll® ExprepTM Plasmid SV Midi (101-226, 101-201)
Visit www.geneall.com or www.geneall.co.kr for FAQ, QnA and more information.
Storage conditionChemical hazard Product specifications
Principle of Method GeneAll® ExprepTM Plasmid Kit Procedures
General considerations
Starting materials Alkaline lysis
Filtration of lysate with EzClearTM Filter Column
Centrifuge in Midi Kits
Protocols for. ExprepTM SV mini
ExprepTM SV Midi
Troubleshooting Guide
Ordering Information
No. of preparation
GeneAll® SV Column type Q
GeneAll® SV Column type T
EzClearTM Filter Column
Protocol Handbook
No. of preparation
GeneAll® SV Column type T
EzClearTM Filter Column
Protocol Handbook
* 10 mM TrisCl, pH 8.5
4 GeneAll® ExprepTM Protocol Handbook
All components in GeneAll® ExprepTM Plasmid kit are manufactured in strictly clean condition, and its degree of cleanness is monitored periodically. Restriction enzyme assay, gene cloning, PCR amplification assay and automated sequencing analysis as quality control are carried out from lot to lot thoroughly, and only the qualified is approved.
Storage conditions
GeneAll® ExprepTM Plasmid kit is shipped at room temperature. All components are stable at room temperature until the date of expiration that is printed on the product label. After addition of RNase A, buffer S1 is stable for 1 year when stored at 4˚C. In cold ambient condition, buffer S2 and S3 may exhibit salt precipitation and this will cause reduction of DNA recover-yields. If so, heat the bottle with occasional swirling in 37 ˚C water bath until completely dissolved.
The buffers included in GeneAll® ExprepTM Plasmid Kit contain the irritant which is harmful when in contact with skin, or when inhaled or swallowed. Care should be taken during handling. Always wear gloves and eye protector, and follow standard safety precautions.
Buffer S3 and AW contain chaotropic salts. It can form highly reactive compounds when combined with bleach. Do NOT add bleach or acidic solution directly to the sample-preparation waste.
GeneAll® ExprepTM Protocol Handbook 5
Product Specifications
GeneAll® ExPrEPTM
PlASMid PurifiCATion KiT
ExprepTM Plasmid Kit
Recommended sample volume
Maximum sample volume
Clearing of lysate
Maximum loading volume
Minimum elution volume
* GeneAll® ExprepTM Plasmid SV Midi kit procedure requires the centrifuge which has a swinging-out bucket and ability of 4,000 5,000 xg.
6 GeneAll® ExprepTM Protocol Handbook
GeneAll® ExPrEPTM
PlASMid PurifiCATion KiT
GeneAll® ExprepTM Plasmid Kit provides easy and rapid method for the smal
and the medium scale preparation of plasmid DNA from bacterial cells. This kit can be used to isolate and purify any plasmid, but works most efficiently when the plasmid is less than 20 kb in size.
All process to prepare pure plasmid DNA takes only about 25 min and
simultaneous processing of multiple samples can be easily performed. Up to 30 ug of pure plasmid can be purified using GeneAll® ExprepTM Plasmid SV mini kit and this pure plasmid DNA is ready for PCR, cloning, fluorescent sequencing, synthesis of labeled hybridization probes, cell transfection, electroporation, and enzymatic restriction analysis without further manipulation.
Principle of Method
GeneAll® ExprepTM Plasmid kit utilizes glass microfiber membrane based on the
modified alkaline lysis method. Alkaline lysis releases plasmid DNA from bacterial cells and degrades RNA, and RNase removes any survived RNA in the lysate. Cell debris and salt precipitates are removed by centrifugation for mini kit and by EzClearTM filter column for Midi kit.
In the presence of high salt, plasmid DNA in cleared lysate binds selectively to
glass microfiber membrane in GeneAll® ExprepTM Plasmid SV column. Bound plasmid DNA is purified in a series of washing steps to eliminate contamination of other bacterial components. Finally elution by low salt buffer or deionized water releases plasmid DNA from the glass microfiber membrane. This simple method eliminates the need for organic solvent extraction and alcohol precipitation.
GeneAll® ExprepTM Protocol Handbook 7
GeneAll® ExprepTM Plasmid SV Kit Procedures
Plasmid SV miniprep
Plasmid SV Midi
8 GeneAll® ExprepTM Protocol Handbook
GeneAll® ExprepTM
Plasmid Purification Kit
General Considerations
The yield and quality of plasmid DNA depends on several factors such as plasmid
copy number, bacterial strain, antibiotics, inoculation and type of culture medium. Wherever possible, plasmids should be purified from bacterial cultures that have been inoculated with a single transformed colony picked from an agar plate.
Usually, the colony is transferred to a small starter culture, which is grown to
late log phase. Aliquots of this culture can be used to prepare small amounts of the plasmid DNA for analysis and/or as the inoculum for a large-scale culture. The conditions of growth of the large-scale culture depend chiefly on the copy number of the plasmid and whether it replicates in a stringent or relaxed fashion. At all times, the transformed bacteria should be grown in selective conditions, i.e., in the presence of the appropriate antibiotics.
The copy number of a plasmid is defined as the average number of plasmids per
bacterial cells under normal growth conditions. Plasmids have own copy number per cell, depending on their origin of replication (replicon) and the size of plasmid DNA. A plasmid replicon can be defined as the smallest piece of plasmid DNA that is able to replicate autonomously and maintain normal copy number by determining whether they are under relaxed or stringent control.
More than 30 different replicons have been identified in plasmids. However,
almost all plasmids used routinely in molecular cloning carry a replicon derived from pMB1. pUC plasmids contain a modified pMB1 replicon, have relaxed control, and replicate to a very high copy number, otherwise pSC101 has stringent control and maintain low-copy number. Generally, high-copy number plasmid will result in higher yield.
Very large plasmids are often maintained at very low copy numbers per cell.
GeneAll® ExprepTM Protocol Handbook 9
GeneAll® ExprepTM Plasmid Kit Procedure is optimized to high-copy number plasmid, so larger starting sample may be needed if low-copy number plasmids are used.
Table1. Replicons carried by various plasmid vectors
Size in bp
Copy number
pBluescript series
pMK16 and derivatives
pBR322 and derivatives
pACYC and derivatives
pSC101 and derivatives
pRK353 and derivatives
Most
E.coli strains can be used to propagate and isolate plasmid DNA. Host
strains such as DH5α and XL1-Blue yield DNA of very high-quality. But some strains, particularly those derived from HB101 (e.g. TG1 and the JM series), release relatively large amount of carbohydrates when they are lysed. Carbohydrates can inhibit the activity of many restriction enzymes and polymerases, if not completely removed.
Many
endA+ strains produce endonuclease I which is encoded in
endA and
cleaves double-strand DNA (See page 13). If endonuclease I is not completely removed during plasmid preparations, the plasmid DNA in eluate is degraded during subsquent incubation in the presence of Mg2+ (e.g. during incubation with restriction enzyme). This problem can be avoided by use of
endA- strains (denoted as
endA1) such as DH5α and XL1-Blue. Extra wash with buffer AW will also help prevent the degradation of DNA.
10 GeneAll® ExprepTM Protocol Handbook
GeneAll® ExprepTM Series is optimized to Luria-Bertani (LB) broth which is the
most widely used culture medium for propagation of
E.coli. Use of other rich broth such as Terrific Broth (TB) or 2xYT will lead to very high cell density. If these media are used, starting sample volume should be reduced not to overload GeneAll® ExprepTM Plasmid SV column and buffer system. Otherwise, the volume of buffer S1, S2 and S3 should be increased for efficient lysis. Overnight culture in TB or 2xYT may yield 2 5 times the number of cells compared to cultures grown in LB broth. TB or 2xYT can be used to obtain more yield of plasmid DNA, in case of low-copy number plasmid.
GeneAll® ExprepTM Protocol Handbook 11
Harvested bacterial culture is resuspended by buffer S1 in the presence of RNase
A. Exposure of bacterial suspensions to the strongly anionic detergent at high pH (Buffer S2, SDS/NaOH) opens the cell wall, denatures chromosomal DNA and proteins, and releases plasmid DNA into the supernatant. Although buffer S2, the alkaline solution, completely disrupts base pairing, the strands of closed circular plasmid DNA are unable to separate from each other because they are topologically intertwined.
As long as the intensity and duration of exposure to high pH (OH-) is not too
great, the two strands of plasmid DNA fall once again into register when the pH is returned to neutral. However, prolonged exposure to denaturing condition causes closed circular DNA to enter an irreversibly denatured state. The resulting collapsed coil, which can not be cleaved with restriction enzymes, migrates through agarose gels at about twice the rate of native superhelical closed circular DNA and stains poorly with intercalating dyes.
During lysis, bacterial proteins, broken cell walls, and denatured chromosomal
DNA become enmeshed in large complexes that are coated with dodecyl sulfate. These complexes are efficiently precipitated from solution by addition of buffer S3 which replaces sodium ions by potassium ions and adjusts the lysate to high-salt binding conditions.
Vigorous handling of lysate may cause the denatured chromosomal DNA to
shear, followed by contamination of genomic DNA. It is important for good result that the solution is gently but thoroughly mixed to ensure complete precipitation.
12 GeneAll® ExprepTM Protocol Handbook
Filtration of lysate with EzClearTM Filter Column
After mixing with buffer S3 the cellular debris and precipitates should be removed
completely not to clog GeneAll® ExprepTM Plasmid SV column in subsequent binding. New patented EzClearTM filter column facilitates the clearance of the lysate by filtration instead of tedious centrifugation which has been used widely in traditional methods.
EzClearTM filter column is included in GeneAll® ExprepTM Plasmid SV Midi Kit.
When working with
endA+ strains, endonucleases can be efficiently removed by
optional wash step with buffer AW to ensure that plasmid DNA is not degraded during storage or enzyme reactions.
Because buffer AW enhances the quality of plasmid DNA by removal of residual
proteins, it is also necessary when working with low-copy plasmids which are generally used with larger culture volume. Buffer PW removes the salt and other cellular components bound nonspecifically to column membrane.
Table 2. The genotype of various
E.coli strains
EndA+ strains
EndA- strains
BL21(DE3), CJ236, HB101, JM83, JM101,
DH1, DH20, DH21, DH5α, JM103,
JM110, LE392, MC1061, NM series, P2392
JM105, JM106, JM107, JM108, JM109,
PR series, RR1, TB1, TG1, BMH71-18,
MM294, SK1590, SRB, XL1-Blue,
ES1301, wild-type and etc.
GeneAll® ExprepTM Protocol Handbook 13
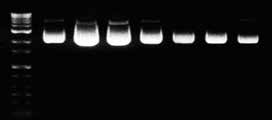
Purified DNA can be eluted in low salt buffer or deionized water as need for
downstream applications. Buffer EB contains 10 mM TrisCl, pH8.5. When using water as eluent, make sure that the pH value is within 7.0 and 8.5.
Because plasmid in water is susceptible to hydrolysis and lacks a buffering agent,
it is recommended to store below -20˚C. The elution volume can be adjusted as necessity, but it has to be over the minimum requirement to soak completely the SV column membrane. For higher concentration of DNA, decrease the volume of elution buffer. For higher yield, increase the volume of elution buffer and repeat the elution step once again. The concentration and yield as the elution volume is shown below.
20 30 50 80 100 120 200
500 800 1000 1500 2000
Elution vol. (ul)
Elution vol. (ul)
Figure 2 . The overall yield and concentration of plasmid DNA depending on the volume of elution. pUC18 plasmid DNA was purified from 3 ml (mini) and 40 ml (Midi) of overnight cultured DH5α using GeneAll® ExprepTM Plasmid SV protocol. Plasmid DNA was eluted with the indicated volume of buffer EB, and resolved on 1 % agarose gel for mini. (Left, data not shown for Midi)
14 GeneAll® ExprepTM Protocol Handbook
Centrifuge in Midi Kit Protocol
GeneAll® ExprepTM Plasmid SV Midi procedures require the conventional
centrifuge which has a swinging-bucket rotor and ability of 4,000 5,000 xg.
Use of fixed-angle rotor will cause inconsistent contact of SV column membrane
with sample mixtures and buffers, and lead to unsatisfactory result.
Low g-force may lead to not only uncomplete removal of ethanol, but also fail of
eluting DNA from the membrane of SV column. Available centrifuges and rotors were listed below, but you can employ any equivalent.
Beckman CoulterInc.
(California, USA)
(Hamburg, Germany)
Industrial Inc.
(Incheon, Korea)
GeneAll® ExprepTM Protocol Handbook 15
GeneAll® ExprepTM Plasmid SV mini
Before Experiment * Unless there is an another indication, all centrifugation steps should
be performed at full speed (>10,000 xg or 10,000 14,000 rpm) in a microcentrifuge at room temperature.
* Add all of RNase solution to buffer S1 before first use.
* Store the buffer S1 at 4˚C after addition of RNase.
* Prepare new 1.5 ml or 2 ml tubes.
* Buffer S2 and S3 may precipitate at cool ambient conditions. If precipitate appears, dissolve it in 37˚C water bath until completely dissolved.
Preparation Of Cleared Lysate
1. Pellet the bacterial culture by centrifugation for 5 min at 10,000 xg in
a tabletop centrifuge. Discard the supernatant as much as possible.
Use appropriate volume of bacterial cultures; up to 5 ml for high copy number plasmid, or up to 10 ml for low copy number plasmid. Bacterial culture should be grown for 16 to 21 hours in LB media containing a selective antibiotics. Use of other rich broth, such as TB or 2xYT, and/or higher culture volume can cause reduction of lysis efficiency or overload of a SV column, resulting in unsatisfactory yields.
Alternatively, bacterial cells can be pelleted repeatedly in 1.5 ml or 2 ml microcentrifuge tube, by centrifugation for 1 min at full speed.
16 GeneAll® ExprepTM Protocol Handbook
2. Resuspend pelleted bacterial cells thoroughly in 250 ul of Buffer S1.
Transfer the suspension to a new 1.5 ml tube.
It is essential to thoroughly resuspend the cell pellet. You don't need to transfer the suspension if the cells have been pelleted in an 1.5 ml tube at previous step.
* Add RNase solution to buffer S1 before first use.
3. Add 250 ul of Buffer S2 and mix by inverting the tube 4 times
(DO NOT VORTEX).
Incubate until the cell suspension becomes clear and viscous, but DO NOT incubate for more than 5 min. It is important to proceed to next step immediately after the lysate becomes clear without any cloudy clumps.
If precipitated material has formed in buffer S2 before use, heat to dissolve at 37˚C. Precipitated buffer S2 may cause significant decrease in DNA recover yield.
4. Add 350 ul of Buffer S3 and immediately mix by inverting the tube
4 6 times (DO NOT VORTEX).
For better precipitation, mix the lysate gently but completely and immediately after addition of buffer S3.
5. Centrifuge for 10 min.
GeneAll® ExprepTM Protocol Handbook 17
Isolation and Purification of plasmid DNA
When using this kit, one of the two methods can be chosen to purify plasmid DNA. Plasmid DNA can be purified using centrifugation to pull the cleared lysate through the SV column. Alternatively, vacuum can be used to force the cleared lysate through the SV column (page 20).
A Centrifugation Protocol
1. Transfer carefully the supernatant to a SV Column by decanting or
pipetting. Centrifuge for 30 sec. Remove the SV Column, discard
the pass-through, and re-insert the SV Column to the collection
tube.
Avoid the white precipitate cotransfering into the SV column.
2. (Optional :) Apply 500 ul of Buffer AW and centrifuge for 30 sec.
Remove the SV Column, discard the pass-through, and reinsert the
SV Column to the collection tube.
This step is necessary to remove any trace of nuclease activity from endA+ strain. The wildtype and some E.coli strains produce endonuclease I which is encoded in gene endA and degrades double-stranded DNA. The E.coli genotype endA1 refers to a mutation in the wildtype endA gene, which produces an inactive form of the nucelase. E.coli strains with this mutation are referred to as endA-.
The absence of endA1 in the genotype-list denotes the presence of the wildtype gene, which expressed an active endonuclease I. The wildtype is indicated as endA+. The genotype of several E.coli strains is shown in table 2 at page 13. When low-copy-plasmid is used, it is strongly recommended to carry out this step, even though endA- strains.
3. Apply 700 ul of Buffer PW and centrifuge for 30 sec. Remove the
SV Column, discard the pass-through, and re-insert the SV Column
to the collection tube.
18 GeneAll® ExprepTM Protocol Handbook
4. Centrifuge for an additional 1 min to remove residual wash buffer.
Transfer the SV Column to a new 1.5 ml tube (Not provided).
This step removes residual ethanol from SV column membrane. Residual ethanol in eluate may inhibit subsequent enzymatic reaction. If carryover of buffer PW occurs, centrifuge again for 1 min before proceeding to next step.
5. Add 50 ul of Buffer EB or deionized distilled water, let stand for
1 min, and centrifuge for 1 min.
Ensure that buffer EB or distilled water is dispensed directly onto the center of spin column membrane for optimal elution of DNA. Eluent volume can be adjusted to 200 ul maximum and it will increase the total yield of plasmid but decrease the concentration of eluate. For higher concentration of eluate, eluent volume can be decreased to 40 ul minimum. The volume of eluate can be smaller than that of eluent and it will not effect the yield. For long-term storage, eluting in buffer EB (10 mM TrisCl, pH 8.5) and storing below -20˚C is recommended. When using water for elution, ensure that the pH of water is within the range of 7.0 8.5. Some larger plasmids (>10 kb) usually may not be eluted optimally unless pre-heated (70˚C) buffer EB or ddH2O is applied for elution. Incubate for 2 min after addition of pre-heated elution buffer.
GeneAll® ExprepTM Protocol Handbook 19
B Vacuum protocol
15 18 in Hg
The vacuum pressure should be in the range of this list.
285 345 mm Hg
Lower vacuum may reduce DNA yield and purity, and
380 460 mbar
too high vacuum pressure may cause to burst the
5.5 6.5 psi
column membrane.
1. Attach the SV Column to a port of the vacuum manifold tightly.
Most commercial vacuum manifold with luer connectors can be used.
2. Transfer the cleared lysate to the SV Column, by pipetting or
Care should be taken not to transfer any of the white precipitate with the supernatant.
3. Switch on vacuum source to draw the solution through the SV
Column. When all liquid has been pulled through the SV Column,
release the vacuum.
4. (Optional:) Apply 500 ul of Buffer AW. Switch on vacuum source
to draw the solution through the SV Column and switch off the
vacuum source.
See the annotation of Step 2 in Centrifugation protocols at page 18.
5. Apply 800 ul of Buffer PW and switch on vacuum source. When all
liquid has been pulled through the SV Column, release the vacuum.
6. Transfer the SV Column to a collection tube (provided).
7. Go to step 4 in Centrifugation Protocol (page 19).
20 GeneAll® ExprepTM Protocol Handbook
GeneAll® ExprepTM Plasmid SV Midi
Before Experiment * Unless there is an another indication, all centrifugation steps should be
performed at room temperature in a centrifuge capable of 4,000 5,000 xg, which has a swinging-bucket rotor (See page 15).
* Add all of RNase solution to buffer S1 before first use.
* Store the buffer S1 at 4˚C after addition of RNase.
* Buffer S2 and S3 may precipitate at cool ambient conditions. If precipitate appears, dissolve it in 37˚C until completely dissolved.
Preparation of Cleared Lysate
1. Pellet the 50 ml of bacterial culture by centrifugation for 5 min
at 10,000 xg in a tabletop centrifuge. Discard the supernatant as
much as possible.
Use appropriate volume of bacterial cultures; For the small sample less than 50 ml or the sample of 50 ml with an OD600 < 2, decrease the volume of buffer S1, S2 and S3 to 2, 2 and 2.8 ml, respectively.
Bacterial culture should be grown for 16 to 21 hours in LB-broth containing a selective antibiotics. If other rich broth, such as TB or 2xYT, and/or higher culture volume more than 100 ml is used, increase the volume of buffer S1, S2 and S3 proportionally, since too high cell density of bacterial cells can cause the reduction of lysis efficiency, resulting in unsatisfactory yields.
GeneAll® ExprepTM Protocol Handbook 21
2. Resuspend pelleted bacterial cells thoroughly in 2.5 ml of Buffer S1.
It is essential to thoroughly resuspend the cell pellet.
* Add RNase solution before first use of the buffer S1.
3. Add 2.5 ml of Buffer S2 and mix by inverting the tube 4 times (DO
NOT VORTEX).
Incubate until the cell suspension becomes clear and viscous, but DO NOT incubate for more than 5 min. It is important to proceed to next step immediately after the lysate becomes clear without any cloudy clumps.
If precipitated material has formed in buffer S2, heat to dissolve at 37˚C. Precipitated buffer S2 may cause significant decrease in DNA recover yield.
4. Add 3.5 ml of Buffer S3 and thoroughly but gently mix by inverting
the tube 4 6 times (DO NOT VORTEX).
For better precipitation and adjustment of binding condition, mix the solution gently but completely and immediately after addition of buffer S3. Incubation on ice may help precipitate the denatured cell components more efficiently; and it may reduce the possibility of the contamination of chromosomal DNA.
5. (Optional :) Centrifuge for 20 min at 4,500 xg (5,000 rpm).
Alternatively, centrifuge for 10 min at 10,000 xg (9,000 rpm) on fixed-angle-rotor centrifuge. Because too high cell density of bacterial cells can cause the clogging of EzClearTM filter on next step, this step may be necessary for large or dense sample.
22 GeneAll® ExprepTM Protocol Handbook
Isolation and Purification of plasmid DNA
When using this kit, one of the two methods can be chosen to purify plasmid DNA. Plasmid DNA can be purified using centrifugation to pull the cleared lysate through the SV column. Alternatively, vacuum can be used to force the cleared lysate through the SV column (page 26).
A A Centrifugation P
Centrifugation P rotocol
1. Pour all of the lysate or the cleared lysate into EzClearTM Filter unit
(blue ring) sitting on a 50 ml conical collection tube (provided).
Incubate for 2 min and centrifuge for 3 min at 1,000 xg (2,200 rpm).
Cellular debris will rise to the top during incubation, and this will assist the clearing of lysate through EzClearTM filter Unit. Failure to perform the incubation may lead to incomplete filtration of lysate. A small amount of liquid can remain trapped in the residual insoluble material, but this will not lead to noteworthy decrease in yield. If the optional centrifugation is performed on step 5 at page 22, transfer only the supernatant into EzClearTM filter Unit (Some debris can be co-transfered).
2. Decant carefully the pass-through fraction to SV Midi Column (red
ring). Centrifuge for 3 min at 1,000 xg (2,200 rpm). Remove the SV
Column, discard the pass-through, and re-insert the SV Column to
the collection tube.
3. Apply 9 ml of Buffer AW and centrifuge for 3 min at 1,000 xg (2,200 rpm).
Remove the SV Column, discard the pass-through, and re-insert
the SV Column to the collection tube.
This step will remove any traces of proteins, carbohydrates, and other cellular components bound nonspecifically to the SV column membrane.
GeneAll® ExprepTM Protocol Handbook 23
4. Apply 12 ml of Buffer PW and centrifuge for 3 min at 1,000 xg
(2,200 rpm). Remove the SV Column, discard the pass-through,
and re-insert the SV Column to the collection tube.
5. Apply 3 ml of Buffer PW and centrifuge for 15 min at 4,500 xg
(5,000 rpm). Transfer the SV Column to a new 50 ml conical tube
(Not provided).
Care must be taken at the removal of SV Midi column from the collection tube so the SV column does not come into contact with the pass-through fraction, as this will result in carryover of ethanol from buffer PW.
Residual ethanol in eluate may interfere with the subsequent reactions. If carryover of ethanol occurs, incubate the SV column for 15 min at RT to evaporate residual ethanol.
6. Add 0.6 ml of Buffer EB or deionized distilled water directly onto
the center of the SV Column membrane. Incubate for 5 min at
room temperature and centrifuge for 5 min at 4,500 xg (5,000 rpm).
Ensure that the buffer EB or distilled water is dispensed directly onto the center of SV column membrane for optimal elution of DNA. The volume of eluent can be decreased to 400 ul for higher concentration of DNA, but this will slightly decrease in overall DNA yield. On the contrary, larger elution-volume will decrease the concentration of eluate but yield slightly more DNA.
For long-term storage, eluting in buffer EB (10 mM TrisCl, pH 8.5) and storing below -20˚C is recommended. When using water for elution, ensure that the pH of water is within 7.0 8.5.
Some larger plasmids (>10 kb) usually may not be eluted optimally unless pre-heated (70˚C) buffer EB or ddH2O is applied for elution. Incubate for 2 min after addition of pre-heated elution buffer.
24 GeneAll® ExprepTM Protocol Handbook
7. (optional :)
A. For higher concentration of eluate; re-load the eluate from step 6 into the
SV column membrane, close the cap, incubate 5 min at room temperature, and centrifuge for 5 min at 4,500 xg (5,000 rpm).
B. For more overall yield; add 0.6 1 ml of fresh buffer EB into the SV column,
close the cap, incubate 5 min at room temperature, and centrifuge for 5 min at 4,500 xg (5,000 rpm).
The first and second eluates can be combined or collected separately as necessity.
GeneAll® ExprepTM Protocol Handbook 25
B Vacuum protocol
B Vacuum protocol
23 26 in Hg
The vacuum pressure should be in the range of this list.
580 660 mm Hg
Lower vacuum pressure may reduce DNA yield and
77 880 mbar
purity, and too high vacuum pressure may cause to
11 12.5 psi
burst the column membrane.
1. Assemble a column stack by nesting EzClearTM Midi Filter Unit
(blue-ring) into the top of SV Midi Column (red-ring). Attach the
assembled Column stack onto a port of the vacuum manifold tightly.
Most commercial vacuum manifold with luer connectors can be used.
2. Decant all of the lysate to EzClearTM Midi Filter Unit and incubate
1 3 min to allow the cellular debris and precipitates to rise to the top.
3. Apply maximum vacuum to draw the solution through the Column
stack. When all liquid has been pulled through the SV Midi Column
at the bottom, slowly release the vacuum.
The lysate will pass through EzClearTM filter Unit and plasmid DNA will be bound to the membrane in Midi SV column. If some of the lysate does not pass through the EzClearTM filter Unit, remove the filter unit, place it into a new 50 ml conical tube, and centrifuge for 3 min at 1,750 xg (3,000 rpm). Then apply the pass-through to the Midi SV column. If the vacuum is released too quickly, the membrane may detach from the SV column. If the membrane becomes detached, tap it down gently with something sterile.
26 GeneAll® ExprepTM Protocol Handbook
4. Discard the upper EzClearTM Filter Unit (blue ring) and apply
9 ml of Buffer AW to SV Midi Column (red ring). Switch on vacuum
source to draw the solution through the SV Midi Column and
slowly release the vacuum.
This step will remove any traces of proteins, carbohydrates, and other cellular components bound nonspecifically to the SV column membrane.
5. Apply 14 ml of Buffer PW and switch on vacuum source. When all
liquid has been pulled through the SV Midi Column, slowly release
the vacuum.
6. Transfer the SV Midi Column to a 50 ml conical tube (provided).
7. Go to step 5 in Centrifugation Protocol (page 24).
GeneAll® ExprepTM Protocol Handbook 27
Troubleshooting Guide
Too many cells in
Cultures should be grown for 16 21 hours
in proper media with antibiotics. Reduce the
plasmid DNA
volume of sample. If rich broth such as Terrific Broth (TB) or 2xYT is used, starting sample volume must be reduced because these me-dia have very high cell density (2 5 times to LB).
Low-copy-number plasmid may yield as lit-
plasmid used
tle as 0.5 ug of DNA from a 5 ml overnight culture. Increase the culture volume or use high-copy-number plasmid or rich broth, if possible.
Poor resuspension of Bacterial cell pellets must be thoroughly re-
bacterial pellets in
suspended in buffer S1.
Buffer S1
Buffer S2 precipi-
Redissolve buffer S2 by warming at 37˚C
Insufficient digestion Excess RNA can interfere the binding of
with RNase
plasmid DNA with GeneAll® Plasmid SV column membrane.
Store buffer S1 at 4˚C after the addition of RNase. If buffer S1 containing RNase is more than a year old, the activity of RNase can be de-creased slightly.
Inadequate elution
DNA is eluted only in low salt condition.
Buffer EB (10 mM TrisCl, pH 8.5) has the optimal elution efficiency, but other elution buffer can be engaged as user's need. Elu-tion efficiency is dependent on pH and the maximum efficiency is achieved between 7.0 and 8.5. When using water for elution, make sure the pH value.
28 GeneAll® ExprepTM Protocol Handbook
Improper centrifuge Swinging-bucket rotor (capable of 4,000
(Midi)
5,000 xg) should be used. Use of fixed-angle rotor may lead to failure of proper contact between the lysate and the column membrane resulting in poor and inconsis-tent yield of DNA.
Low purity
Contamination of
When the cleared lysate is transferred to
precipitate when
GeneAll® ExprepTM Plasmid SV column, en-
sure that any precipitate does not contain to the transfer.
Improper centrifuge Swinging-bucket rotor (capable of 4,000
(Midi)
5,000 xg) should be used instead of fixed angle rotor.
Chromosomal Mis-handling of the
Vigorous vortexing after addition of buffer S3
DNA contam-
lysate after addition can cause shearing of chromosomal DNA fol-
of Buffer S3
lowed by chromosomal DNA contamination.
Handle gently the lysate after addition of buffer S3. Simple inverting and rotating tube to cover walls with lysate is sufficient for mixing.
Smearing of
Too long lysis time
Too long lysis under buffer S2 can cause chro-
plasmid DNA
mosomal DNA contamination. Proceed to next step immediately after no more clumps are visible in the lysate. Lysis time should not be over 5 min in any case.
Vigorous mixing in
Vigorous handling after addition of buffer
Buffer S2
S2 can lead to irreversible denaturation of plasmid DNA. Gentle inverting and rotating tube to cover walls with viscous lysate is suf-ficient for mixing.
Lysate filtered
Excessive salt-precip- The biomass in starting sample is small. De-
by EzClearTM is
itates in lysate
crease the volume of buffers during alkaline
not clear
lysis. Otherwise, increase the amount of starting sample.
GeneAll® ExprepTM Protocol Handbook 29
Troubleshooting Guide
RNA Contam-
RNase omitted or
RNase solution should be added to buffer
S1 before first use. If buffer S1 containing RNase is more than a year old, the activity of RNase can be decreased. Add additional RNase (working concentration = 100 ug/ml). Buffer S1 containing RNase should be stored at 4˚C.
Too many cells in
Reduce the sample volume. Too many cells
may not be subjected properly to RNase digestion.
High salt
Improper wash step Ensure the wash step in protocol.
Alternatively, incubate for 5 min at room
in eluate
temperature after applying buffer PW in wash step.
Plasmid DNA
Nuclease contamina- For endA+ strains such as HB101 and the
degradation
JM series (page13) , washing with buffer AW should be carried out properly.
DNA floats
Ethanol is not
Ensure that washing steps are performed
out of well
completely removed properly. GeneAll® ExprepTM Plasmid SV
while loading
during wash steps
column membrane should be completely
of agarose gel
dried via additional centrifugation or air-drying for good result.
Enzymatic
High salt
Ensure that washing step was carried out
reaction is not
concentration in
just in accordance with the protocols. Re-
performed
peat of washing step may help to remove high salt in eluate.
well with puri-
fied DNA
Low purity of DNA
See"Low purity" at page 29.
Residual ethanol in
Ensure that the washing steps are per-
formed properly. GeneAll® ExprepTM Plas-mid SV column membrane should be com-pletely dried via additional centrifugation or air-drying.
30 GeneAll® ExprepTM Protocol Handbook
GeneAll® ExprepTM Plasmid SV mini
1. Pellet cells by centrifugation2. Resuspend in 250 ul of Buffer S13. Add 250 ul of buffer S2 and mix by inverting4. Add 350 ul of buffer S3 and mix by inverting5. Centrifuge for 10 min6. Transfer the cleared lysate to SV column and centrifuge for 30 sec7. (Optional) Add 500 ul of buffer AW and centrifuge for 30 sec8. Add 700 ul of buffer PW and centrifuge for 30 sec9. Centrifuge for additional 1 min
10. Apply 50 ul of buffer EB and centrifuge for 1 min
GeneAll® ExprepTM Plasmid SV Midi
1. Pellet cells by centrifugation2. Resuspend in 2.5 ml of buffer S13. Add 2.5 ml of buffer S2 and mix by inverting4. Add 3.5 ml of buffer S3 and mix by inverting5. (Optional) Centrifuge for 20 min at 4,500 xg (5,000 rpm)6. Transfer the lysate (step 4) or the cleared lysate (step 5) to EzClearTM column
(blue ring), let stand for 2 min and centrifuge for 3 min at 1,000 xg (2,200 rpm)
7. Transfer the pass-through to SV Midi column (red ring) and centrifuge for 3 min at
1,000 xg (2,200 rpm)
8. Add 9 ml of buffer AW and centrifuge for 3 min at 1,000 xg.
9. Add 12 ml of buffer PW and centrifuge for 3 min at 1,000 xg.
10. Add 3 ml of buffer PW and centrifuge for 15 min at 4,500 xg.
11. Apply 500 ul of buffer EB , let stand for 5 min and centrifuge for 5 min at 4,500 xg.
GeneAll® ExprepTM Protocol Handbook 31
Scale Size Cat. no. Type
Scale Size Cat. no. Type
Hybrid-QTM for rapid preparation of plasmid DNA
ExgeneTM for isolation of total DNA
Plasmid Rapidprep
ExprepTM for preparation of plasmid DNA
for preparation of highly pure plasmid DNA
(Low Endotoxin)
Genomic DNA micro
(Endotoxin Free)
ExpinTM for purification of fragment DNA
GenExTM for isolation of total DNA
ExgeneTM for isolation of total DNA
GenExTM Blood
GenExTM Cell
GenExTM Tissue
Tissue plus! SV
32 GeneAll® ExprepTM Protocol Handbook
Scale Size Cat. no. Type
Scale Size Cat. no. Type
GenExTM for isolation of total DNA
AmpONETM for PCR amplification
GenExTM Plant
500 U 531-050 (2.5 U/㎕)
GenExTM Plant plus!
500 U 551-050 (2.5 U/㎕)
for preperation of PCR-template without extraction
500 U 552-050 (2.5 U/㎕)
RNA series for preparation of total RNA
521-200 lyophilized
Hybrid-RTM Blood RNA mini 50
522-200 lyophilized
RiboclearTM plus!
Taq Premix (w/o dye)
524-200 lyophilized
-Taq Premix (w/o dye) 96 tubes 20 ㎕
Ribospin TM vRD plus! mini 50
500 ㎕ 509-020 2.5 mM each
Ribospin TM Plant
(set of dATP, dCTP, dGTP and dTTP)
AmpMasterTM for PCR amplification
AmpONETM for PCR amplification
541-010 0.5 ml x 2 tubes
541-050 0.5 ml x 10 tubes
Taq DNA polymerase
500 U 501-050 (2.5 U/㎕)
542-010 0.5 ml x 2 tubes
542-050 0.5 ml x 10 tubes
545-010 0.5 ml x 2 tubes
-Taq DNA polymerase
500 U 502-050 (2.5 U/㎕)
HS-Taq Master mix
545-050 0.5 ml x 10 tubes
* Each dNTP is available
Pfu DNA polymerase
500 U 503-050 (2.5 U/㎕)
GeneAll® ExprepTM Protocol Handbook 33
34 GeneAll® ExprepTM Protocol Handbook
GeneAll® ExprepTM Protocol Handbook 35
www.geneall.com
GeneAll Bldg., 303-7 Dongnam-ro
Songpa-gu, Seoul, Korea 138-859
E-mail : [email protected]
Tel : 82-2-407-0096
Fax : 82-2-407-0779
Edited by BnP
ⓒ2013 GeneAll Biotechnology, All right reserved
Designed by Park Eun Ah
Source: http://geneall.cambio.co.uk/library/images/html_images/GeneAll/2013_plasmid_web.pdf
The Commission on Higher Education in collaboration with the Philippine Normal University INITIAL RELEASE: 13 JUNE 2016 Teaching Guide for Senior High School GENERAL SPECIALIZED SUBJECT ACADEMIC - STEM This Teaching Guide was collaboratively developed and reviewed by educators from public and private schools, colleges, and universities.
Effective February 6, 2015 U.S. lithium battery regulations Regulations applicable to shipments of as Dangerous Goods do not require a lithium batteries within the United States UPS Dangerous Goods contract, provided Lithium battery types have changed. Compliance with the restrictions below are satisfied. There are two major kinds of lithium new regulations is mandatory effective

