Impactfactor.org
Available online on www.ijddt.com
International Journal of Drug Delivery Technology 2014; 4(4); 58-66
Microsponges: An Overview
*Hamid Hussain, Divya Juyal, Archana Dhyani
Himalayan Institute of Pharmacy and Research Rajawali Dehradun, India
Available Online: 29th September 2014
ABSTRACT
Microsponge and Nanosponge delivery System was originally developed for topical delivery of drugs can also be used for
controlled oral delivery of drugs using water soluble and bioerodible polymers. Microsponge delivery system (MDS) can
entrap wide range of drugs and then release them onto the skin over a time by difussion mechanism to the skin. It is a
unique technology for the controlled release of topical agents and consists of nano or micro porous beads loaded with active
agent and also use for oral delivery of drugs using bioerodible polymers.
Keywords: Microsponge drelivery system (MDS), Nanosponge. Bioerodible.
response to triggers including rubbing, pH, friction,
Microparticles and nanoparticles have been increasingly
moisture and ambient skin temperature[5].
investigated to achieve targeted and sustained release of
Advantages of microsponges:
drugs [1] and among this microsponge is one of the recent
Microsponges are biologically safe and offer unique
and an innovative noval approach to deliver a drug in a
advantage of programmable release.
controlled way.
They offer entrapment of numerous ingredients and is
They are tiny, sponge like spherical particles that consist
believed to contribute elegance and enhanced
of a myriad of interconnecting voids within a non-
collapsible structure with a
large porous surface
Have the capacity to adsorb or load a high degree of
Microsponge delivery systems (MDS) that can precisely
active materials into the particle or unto its surface.
control the release rates or target drugs to a specific body
Microsponges are stable over a ph range of 1-11 and
site have an enormous impact on the health care system.
upto temperature of 130 ºc
The microsponge drug delivery technology is widely
They are self sterilizing as average pore size is 0.25 µm
applicable to the dermatological drug delivery products.
where bacteria cannot penetrate.
But MDS also expands its application in oral drug delivery,
Microsponges are capable of absorbing skin secretions
bone and tissue engineering, in Detecting the diseases and
so reducing the oiliness of the skin upto 6 times of its
in RNAi silencing. New classes of pharmaceuticals,
biopharmaceuticals (peptides, proteins and DNA-based
With size 10-25 microns in diameter it is capable of
therapeutics) are fueling the rapid evolution of drug
delivery technology. Thus MDS is a very emerging field
which is needed to be explored [2]
. Microsponges are
The drug releases in microsponges y the external stimuli
porous, polymeric microspheres that are mostly used for
like ph, temperature, and rubbing.
prolonged topical
Microsponges have several advantages over topical
designed to deliver a pharmaceutically active ingredient
preparations in being nin-allergic, non-toxic, non-irritant
efficiently at minimum dose and also to enhance stability,
and non-mutagenic.
reduce side effects, and modify drug release profiles [3].
it is a polymeric microspheres that acquire the flexibility
Microsponges are all ways stable i.e, thermal, physical
to entrap a wide variety of active ingredients such as
and chemical [6].
emollients, fragrances, sunscreens, essential oils, anti-
These are compatible with the majority of vehicles and
infective, anti-fungal and anti-inflammatory agents etc and
are used as a topical carrier system[4]. Resembling a true
These systems have higher payload up to 50 to 60% [5].
sponge, each microsphere consists of an innumerable of
Advantages of Microsponges over Other Formulations
interconnecting voids within a non-collapsible structure
Microsponges have several other advantages over other
with a large porous surface. It is a unique technology for
preparations available in the market. Comparison between
the controlled release of topical agents which consists of
some of them are given below as such;
microporous beads normally 10-25 microns in diameter,
Advantages over conventional formulations: Conventional
loaded with active ingredients that is subsequently releases
formulations of topical drugs are intended to work on the
them onto the skin over a time in a controlled manner or in
*Author for correspondence: E-mail: [email protected]

Hamid Hussain et al. / Microsponges: An Overview…
outer layers of the skin. Such products release their active
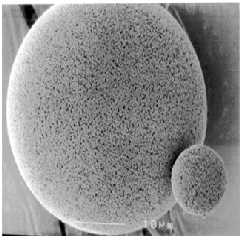
Fig. 1: View of microsponge
Fig. 2: Highly porous nature of a Microsponge
ingredients upon application, producing a highly
It should exhibit complete miscibility in monomer or
concentrated layer of active ingredient that is rapidly
have the ability to be miscible using the least amount of
adsorbed. When compared to the conventional system.
a water immiscible solvent.
Microsponge system can prevent excessive accumulation
Must be inert to monomers and do not increase the
of ingredient within the epidermis and the dermis.
viscosity of the preparation during formulation.
Potentially, the MDDS can reduce significantly the
It should be water immiscible or almost slightly soluble.
irritation of effective drugs without reducing their efficacy.
The solubility of active ingredients in the vehicle should
Advantages over microencapsulations and liposomes: The
be minimum; otherwise the microsponge will be
MDS has advantages over other technologies like
diminished by the vehicle before application.
microencapsulations and liposomes. Microcapsules cannot
It should maintain (preserve) the spherical structure of
usually control the release rate of actives. Once the wall is
ruptured, the actives contained within microcapsules will
It should be stable in polymerization conditions.
be released.
Only 10 to 12% w/w microsponge can be incorporated
Liposomes suffer
lower payload, difficult
into the vehicle to eliminate cosmetic delinquent.
formulation, limited chemical stability and microbial
Payload and polymer design of the microsponges for the
instability, while microsponges system in contrast to the
active must be adjusted to obtain the desired release rate
above system has several advantages like stable over a ph
of a given period of time. [9].
range of 1-11 and upto temperature of 130 ºc, stable
Methods of preparation for microsponges: Initially, drug
thermally, physicaly and chemically, have higher payload
loading in microsponges is mainly take place in two ways
up to 50 to 60%, have average pore size is 0.25 µm whwre
depending upon the physicochemical properties of drug to
bacteria cannot penetrate[7].
be loaded. If the drug is typically an inert non-polar
Advantages over ointments:
Ointments are often
material which will generate the porous structure then, it is
aesthetically unappealing, greasiness; stickiness etc. That
known as porogen. A Porogen drug neither hinders the
often results into lack of patient compliance. These
polymerization process nor become activated by it and also
vehicles require high concentrations of active agents for
it is stable to free radicals is entrapped with one-step
effective therapy because of their low efficiency of
delivery system, resulting into irritation and allergic
Microsponges are suitably prepared by the following
reactions in significant users. Other drawbacks of topical
formulations are uncontrolled evaporation of active
Liquid-liquid suspension polymerization: The porous
ingredient, unpleasant odor and potential incompatibility
microspheres are prepared by suspension polymerization
of drugs with the vehicles, when microsponge system
method in liquid-liquid systems. In their preparation, the
maximize amount of time that an active ingredient is
monomers are first dissolved along with active ingredients
present either on skin surface or within the epidermis,
in a suitable solvent solution of monomer and are then
while minimizing its transdermal penetration into the
dispersed in the aqueous phase, which consist of additives
(surfactant, suspend-ing agents, etc. to aid in formation of
Characters of Drugs to be entrapped in the Microsponges:
suspension). The polymerization is then initiated by adding
There are certain requirements that should be fulfilled (or
catalyst or by increasing temperature or irradiation. The
considered) when active ingredients are entrapped into
various steps in the preparation of microsponges are
summarized as.
Selection of monomer or combination of mono-mers.
IJDDT, October-December 2014, 4(4), 58-66
Hamid Hussain et al. / Microsponges: An Overview…
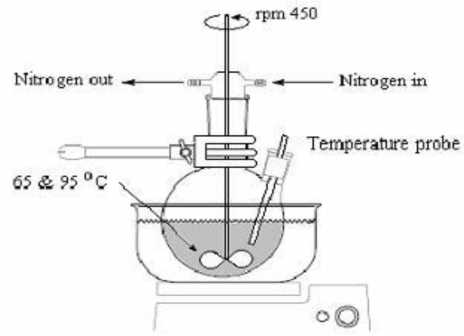
Fig 3: Instrument set up for suspension polymerization technique
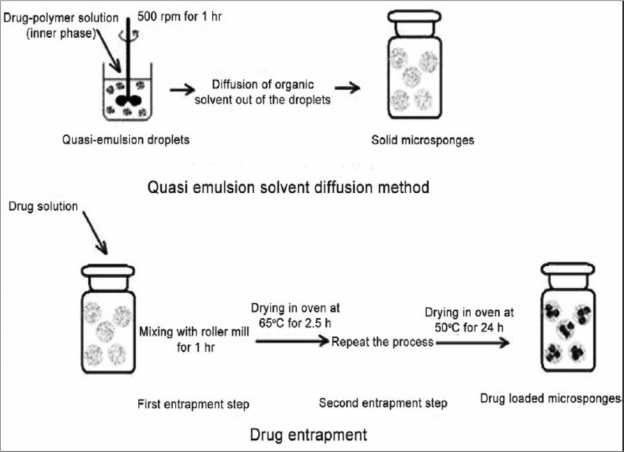
Fig 4: Quasi-emulsion solvent diffusion method set up.
Formation of chain monomers as polymerization begins.
Binding of bunches to form microsponges. [10]
Formation of ladders as a result of cross linking between
Quasi-emulsion solvent diffusion method: (Top down
chain monomers.
approach): This is top-down approach starting with
Folding of monomer ladder to form spherical particles.
preformed polymer. This process involved formation of
Agglomeration of microspheres, which give rise to
quasi-emulsion of two different phases i.e. internal phase
formation of bunches of microspheres.
IJDDT, October-December 2014, 4(4), 58-66
Hamid Hussain et al. / Microsponges: An Overview…
and external phase similar to emulsions. The internal phase
Determination of true density: The true density of
of drug--polymer solution made in a volatile solvent like
Microsponges can be measured using an ultra-pycnometer
ethanol or acetone or dichloromethane was added to
under helium gas and is calculated from a mean of repeated
external phase comprising the aqueous polyvinyl alcohol
(PVA) solution with vigorous stirring. Triethylcitrate
Pore structure: Porosity parameters of microsponges are
(TEC), which was added at an adequate amount in order to
essential in monitoring the intensity and the duration of
facilitate plasticity. Stirring lead to the formation of
active ingredient effect. Average pore diameters, shape
discrete emulsion globules called quasi-emulsion globules.
and morphology of the pores can be determined by using
Solvent was then extracted out from these globules to form
mercury intrusion porosimetry technique. The effect of
pore diameter and volume on the rate of drug release from
Following sufficient stirring, the mixture was then filtered
microsponges can also be studied using the same
to separate the microsponges. The microsponges were then
technique. [17].
dried in an air heated oven. Conceptually, the finely
Compatibility studies: The drug-excipient compatibility
dispersed droplets of the polymeric solution of the
studies are carried out in order to ensure that there is no
drug(dispersed phase) get solidified in aqueous phase via
inadvertent reaction between the two when formulated into
counter diffusion of organic solvent and water out of and
a dosage form. These studies are commonly carried out by
into the droplets. The diffused aqueous phase within the
recording the differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) of
droplets decreased the drug and polymer solubility
both the chemicals viz., API and excipient individually and
resulting in the co-precipitation of both the components
also together and checking for any addition or deletion of
and continued diffusion of the organic phase results in
any peaks or troughs. For DSC approximately 5 mg
further solidification, producing matrix-type porous
samples can be accurately weighed into aluminium pans
and sealed and can be run at a heating rate of 15oC/min
suspension polymerization method, this method offered
over a temperature range 25–430oC in atmosphere of
the advantage of less exposure of the drug to the ambient
nitrogen. [18,19].
conditions, low solvent residues in the product because the
spectroscopy can also reveal the
solvent get extracted out due to its solubility in aqueous
incompatibilities
media or due to its volatile nature. [11,12,13]
Compatibility of drug with reaction adjuncts can also be
Evaluation Parameters
studied by thin layer chromatography (TLC) and FT-IR
Particle size and size distribution: Particle size and size
[35]Effect of polymerization on crystallinity of the drug
distribution are evaluated using either an optical
can be studied by powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) and
microscope or an electron microscope. This is an
Differential Scanning Colorimetry (DSC). [20].
extremely crucial step, as the size of the particles greatly
Polymer/ Monomer composition: Factors such as particle
affects the texture of the formulation and its stability. Free-
size, drug loading, and polymer composition govern the
flowing powders with fine aesthetic attributes are possible
drug release from Microsponges. Polymer composition of
to obtain by controlling the size of particles during
the Microsponges Drug Delivery system can affect
polymerization. Particle size analysis of loaded and
partition coefficient of the entrapped drug between the
unloaded Microsponges can be performed by laser light
vehicle and the Microsponges system and hence have
diffractometry or any other suitable method. The values
direct influence on the release rate of entrapped drug.
(d50) can be expressed for all formulations as mean size
Release of drug from Microsponge systems of different
range. Cumulative percentage drug release from
polymer compositions can be studied by plotting
Microsponges of different particle size will be plotted
cumulative % drug release against time. Release rate and
against time to study effect of particle size on drug release.
total amount of drug released from the system composed
of methyl methacrylate/ ethylene glycol dimethacrylate is
Morphology and Surface topography of SPM: For
slower than styrene/divinyl benzene system. Selection of
morphology and surface topography, various techniques
monomer is dictated both by characteristics of active
have been used like photon correlation spectroscopy
ingredient ultimately to be entrapped and by the vehicle
(PCS), Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission
into which it will be dispersed. Polymers with varying
electron microscopy (TEM) etc. SEM is used widely for
electrical charges or degrees of hydrophobicity or
which prepared Microsponges are coated with gold–
lipophilicity may be prepared to provide flexibility in the
palladium under an argon atmosphere at room temperature
release of active ingredients. Various monomer
and then the surface morphology of the Microsponges is
combinations will be screened for their suitability with the
studied. [15].
drugs by studying their drug release profile. [21].
Determination of loading efficiency and production yield:
Resiliency (viscoelastic properties) of
The loading efficiency (%) of the Microsponges can be
Microsponges can be modified to produce beadlets that is
calculated according to the following equation:
softer or firmer according to the needs of the final
The production yield of the microparticles can be
formulation. Increased cross-linking tends to slow down
determined by calculating accurately the initial weight of
the rate of release. Hence resiliency of Microsponges is
the raw materials and the last weight of the SPM obtained.
studied and optimized as per the requirement by
considering release as a function of crosslinking with time
IJDDT, October-December 2014, 4(4), 58-66
Hamid Hussain et al. / Microsponges: An Overview…
Table 1: Marketed formulations of microsponges[38,39]Product name
Dermik Laboratories, Inc.
Carac Cream contains 0.5% fluorouracil; with 0.35% being
Berwyn , PA 19312 USA
incorporated into a patented porous microsphere consisted ofmethyl methacrylate / glycol dimethacrylate cross-polymer anddimethicone. Carac is a once-a-day topical prescription productfor the treatment of actinic keratosis (AK) that is characterizedby common pre-cancerous skin condition caused byoverexposure to the sun.
Salicylic Peel 20
Retin-A-Micro contains 0.1% and 0.04% tretinoin entrapped into
a patented porous microsphere consisted of methyl methacrylate/glycol dimethacrylate cross-polymer to enable inclusion of theactive ingredient, tretinoin, in an aqueous gel. This formulationis used for the topical treatment of acne vulgaris.
Salicylic acid 20%, microsponge technology has excellentexfoliation and used for stimulation of the skin for more resistantskin types or for faster results. It will considerably improvepigmentation, fine lines and acne concerns. Salicylic acid moveseasily through the pores, clearing them out while reducinginflammation. This treatment effectively combats acne leavingan amazingly smooth and clear complexion.
Lightweight cream with a retinol (Vitamin A) in MDS, dual-
system delivers both immediate and time released wrinkle-
fighting action. Clearly diminishes appearance of fine lines,
wrinkles & skin discolorations associated with aging.
Retin-A-Micro contains 0.1% and 0.04% tretinoin entrapped into
a patented porous microsphere consisted of methyl methacrylate/glycol dimethacrylate cross-polymer to enableinclusion of the active ingredient, tretinoin, in an aqueous gel.
This formulation is used for the topical treatment of acnevulgaris.
The MicroPeel ® Plus procedure stimulates cell turnover through
the application of salicylic acid in the form of microcrystals usingMicrosponge® technology. These microcrystals target the exactareas on the skin that need improvement. The MicroPeel Plusaggressively outperforms other superficial chemical peels byfreeing the skin of all dead cells while doing no damage to theskin.
A night time treatment cream with Microsponge technology
using a stabilized formula of pure retinol, Vitamin A. Continued
use of Retinol 15 will result in the visible diminishment of finelines and wrinkles, a noticeable improvement in the skindiscolorations due to aging, and enhanced skin smoothness.
SDR Pharmaceuticals, Inc.,
Lactrex™ 12% Moisturizing Cream contains 12% lactic acid as
Andover , NJ , U.S.A. 07821
the neutral ammonium salt, ammonium lactate. Microsponge®
technology has been included for easy application and longlasting moisturization. Lactrex™ also contains water andglycerin, a natural humectant to soften and help moisturize drys,flaky, cracked skin.
The Microsponge® system uses microscopic reservoirs thatentrap hydroquinone and retinol.
The microsponges release these ingredients into the skingradually throughout the day. This provides the skin withcontinuous exposure to hydroquinone and retinol over time,which may minimize skin irritation. EpiQuin Micro is aprescription moisturizing fading cream that reducesthe impact of these conditions known as melasma, postinflammatory hyper pigmentation or solar lentigines. Also helpin Age spots, Sun spots and Facial discoloration.
IJDDT, October-December 2014, 4(4), 58-66
Hamid Hussain et al. / Microsponges: An Overview…
Table 1: Marketed formulations of microsponges[38,39]Product name
Oil free matte block
This invisible oil-free sunscreen shields the skin from damaging
UV sun rays while controlling oil production, giving you ahealthy matte finish. Formulated with microsponge technology,Oil free matter block absorbs oil and preventing shine withoutany powdery residue.
Sportscream RS and
Embil Pharmaceutical Co.
Topical analgesic-anti-inflammatory and counterirritant actives
in a microsponge® deliverysystem (MDS) for the management of musculoskeletalconditions.
Oil Control Lotion
Fountain Cosmetics
A feature-light lotion with technically advanced microspongesthat absorb oil on the skin's surface during the day, for a mattefinish. Eliminate shine for hours with this feature-weightlotion, formulated with oil-absorbing Microsponge technology.
The naturally- antibiotic Skin Response Complex soothesinflammation and tightness to promote healing. Acne-Prone,oily skin conditions.
Kinetics of release: To determine the drug release
intervals and analyzed using suitable method of assay
mechanism and to compare the release profile differences
(Embil and Nacht, 1996; Jelvehgari et al., 2006). To
among microsponges, the drug released amount versus
determine the drug release kinetics and investigate its
time was used. The release data were analysed with the
mechanism from microsponges, the release data are fitted
following mathematical models:
to different kinetic models. The kinetic models used are;
Q= k1tn or log Q= log k1 + n log t ………………Equation
first order, zero order, Higuchi and Korsmeyer- Peppas
models (Higuchi, 1963; Wagner, 1969; Korsmeyer et al.,
Where Q is the amount of the released at time (h), n is a
1983; Peppas, 1985). The goodness of fit was evaluated
diffusion exponent which indicates the release mechanism,
using the determination coefficient (R2) values. [24]
and k1 is a constant characteristic of the drug–polymer
Safety Considerations
interaction. From the slope and intercept of the plot of log
Safety studies of microsponges can be confirmed by;
Q versus log t, kinetic parameters n and k1 were calculated
Allergenicity in guinea pigs
For comparison purposes, the data was also subjected to
Eye irritation studies in rabbits
Equation (2), which may be considered a simple, Higuchi
Mutagenicity in bacteria
type equation.
Oral toxicity studies in rats.
Q = k2t0.5 +C ………………… Equation (2)
Skin irritation studies in rabbits. [25,26,27]
Equation (2), for release data dependent on the square root
Applications of Microsponge Systems: Microsponge
of time, would give a straight line
delivery systems are used to enhance the safety,
release profile, with k2 presented as a root time dissolution
effectiveness and aesthetic quality of topical prescription,
rate constant and C as a constant. [23].
over-the-counter and personal care products. Products
under development or in the market place utilize the
In vitro release studies, release kinetics and mechanism:
Topical Microsponge systems in three primary ways:
In vitro release studies can be performed using United
As reservoirs releasing active ingredients over an
States Pharmacopeial (USP) dissolution apparatus
extended period of time,
equipped with a modified basket consisted of 5 μm
As receptacles for absorbing undesirable substances,
stainless steel mesh at 37°C. The release medium is
such as excess skin oils, or
selected according to the type of formulation that is, topical
As closed containers holding ingredients away from the
or oral, while considering solubility of active ingredients
skin for superficial action.
to ensure sink conditions. Sample aliquots are withdrawn
Releasing of active ingredients from conventional topical
from the medium and analyzed by suitable analytical
formulations over an extended period of time is quite
method at regular intervals of time. The drug release from
topical preparations (for example, creams, lotions and
Cosmetics and skin care preparations are intended to work
emulgels) containing microsponges can be carried out
only on the outer layers of the skin. The typical active
using Franz diffusion cells. Dialysis membrane is fitted
ingredient in conventional products is present in a
into place between the two chambers of the cell. A
relatively high concentration and, when applied to the skin,
predetermined amount of formulation is
may be rapidly absorbed. The common result is over-
mounted on the donor side of Franz cell. The receptor
medication, followed by a period of under-medication until
medium is continuously stirred at and thermostated with a
the next application. Rashes and more serious side effects
circulating jacket. Samples are withdrawn at different time
can occur when the active ingredients rapidly penetrate
below the skin's surface. Microsponge technology is
IJDDT, October-December 2014, 4(4), 58-66
Hamid Hussain et al. / Microsponges: An Overview…
designed to allow a prolonged rate of release of the active
microsponges were prepared by the direct compression
ingredients, thereby offering potential reduction in the side
method. Results indicated that compressibility was much
effects while maintaining the therapeutic efficacy. [28].
improved in the physical mixture of the drug and polymer;
Microsponge for topical delivery: The Microsponge
due to the plastic deformation of the sponge-like
systems are based on microscopic, polymer-based
microsponge structure, producing mechanically strong
microspheres that can bind, suspend or entrap a wide
tablets. Colon-specific, controlled delivery of flurbiprofen
variety of substances and then be incorporated into a
was conducted by using a commercial Microsponge®
formulated product, such as a gel, cream, liquid or powder.
5640 system. In vitro studies exhibited that compression-
A single Microsponge is as tiny as a particle of talcum
coated colon-specific tablet formulations started to release
powder, measuring less than one-thousandth of an inch in
the drug at the eighth hour, corresponding to the proximal
diameter. Like a true sponge, each microsphere consists of
colon arrival time, due to addition of the enzyme,
a myriad of interconnecting voids within a non-collapsible
following a modified release pattern, while the drug
structure that can accept a wide variety of substances. The
release from the colon-specific formulations prepared by
outer surface is typically porous, allowing the controlled
pore plugging the microsponges showed an increase at the
flow of substances into and out of the sphere.
eighth hour, which was the point of time when the enzyme
Several primary characteristics, or parameters, of the
addition was made. [33,34].
Microsponge system can be defined during the production
Microsponge for Bone and Tissue Engineering: Bone-
phase to obtain spheres that are tailored to specific product
substitute compounds were obtained by mixing pre
applications and vehicle compatibility. Microsponge
polymerized powders of polymethylmethacrylate and
systems are made of biologically inert polymers. Extensive
liquid methylmethacrylate monomer with two aqueous
safety studies have demonstrated that the polymers are
dispersions of tricalcium phosphate grains and calcium
non-irritating, nonmutagenic, non-allergenic, non-toxic
deficient hydroxyapatite powders. The final composites
and non-biodegradable. As a result, the human body
appeared to be porous and acted as microsponges. Basic
cannot convert them into other substances or break them
fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) incorporated in a collagen
down. Although they are microscopic in size, these
sponge sheetwas sustained released in the mouse sub-cutis
systems are too large to pass through the stratum corneum
according to the biodegradation of the sponge matrix, and
when incorporated into topical products [29]. Benzoyl
exhibited local angiogenic activity in a dose-dependent
peroxide (BPO) is commonly used in topical formulations
manner. The injection of collagen microsponges
for the treatment of acne,with skin irritation as a common
incorporating bFGF induced a significant increase in the
side effect. It has been shown that controlled release of
blood flow, in the murine ischemic hind limb, which could
BPOfrom a delivery system to the skin could reduce the
never have been attained by the bolus injection of bFGF.
side effect while reducing percutaneous absorption.
These results suggest the significance and therapeutic
Therefore, microsponge delivery of Benzoyl peroxide was
utility of the type I collagen as a reservoir of bFGF. [35,36]
developed using an emulsion solvent diffusion method by
Future Prospects: Microsponge drug delivery system holds
adding an organic internal phase containing benzoyl
a promising opportunity in various pharmaceutical
peroxide, ethyl cellulose and dichloromethane into a
applications in the upcoming future as it has unique
stirred aqueous phase containing polyvinyl alcohol and by
properties like enhanced produc
suspension polymerization of styrene and divinyl benzene
elegancy, extended release, improved drug release profile,
.The prepared microsponges were dispersed in gel base
reduced irritation, improved physical, chemical and
and microsponge gels are evaluated for anti-bacterial and
thermal stability which makes it flexible to develop novel
skin irritancy. The entrapped system released the drug at
product forms. The real challenge in future is the
slower rate than the system containing free BPO. Topical
development of the delivery system for the oral peptide
delivery system with reduced irritancy was successfully
delivery by varying ratio of polymers. The use of
bioerodible and biodegradable polymers for the drug
Microsponge for oral delivery: In oral applications, the
delivery is enabling it for the safe delivery of the active
microsponge system has been shown to increase the rate of
material. As these porous systems have also been studied
solubilization of poorly water-soluble drugs by entrapping
for the drug delivery through pulmonary route which
such drugs in the microsponge system's pores. As these
shows that these system can show effective drug release
pores are very small, the drug is in effect reduced to
even in the scarce of the dissolution fluid thus colon is an
microscopic particles and the significant increase in the
effective site for targeting for drug release. These carriers
surface area thus greatly increases the rate of
also require to be developed for alternative drug
solubilization. Controlled oral delivery of ibuprofen
administration routes like parenteral and pulmonary route.
microsponges is achieved with an acrylic
These particles can also be used as the cell culture media
polymer, Eudragit RS, by changing their intraparticle
thus can also be employed for stem cell culture and cellular
chlorpheniramine
regenaration in the body. Due to their elegance, these
microsponges, is prepared by the dry impact blending
carrier systems have also found their application in
method, for oral drug delivery. Controlled oral delivery of
cosmetics. These developments enabled researchers to
Ketoprofen prepared by quasi-emulsion solvent diffusion
utilize them variably. These novelties in formulation also
method with Eudragit RS 100 and afterwards tablets of
open new ways for drug delivery. [37]
IJDDT, October-December 2014, 4(4), 58-66
Hamid Hussain et al. / Microsponges: An Overview…
characterization and release studies. International
MDS has become highly competitive and rapidly evolving
Journal of Pharmaceutics (2006)124-132.
technology and more and more research are carrying out to
12. Kawashima Y, Niwa T, Takeuchi H, Hino T, Ito Y.
optimize cost-effectiveness and efficacy of the therapy.It
Control of Prolonged Drug Release and Compression
is a unique technology for the controlled release of topical
Properties of Ibuprofen Microsponges with Acrylic
agents and consists of microporous beads loaded with
active agent and also use for oral as well as
Intraparticle Porosity. Chemical and pharmaceutical
biopharmaceutical drug delivery. Microsponge delivery
bulletin. (1992) 196-201
systems that can precisely control the release rates or target
13. Comoglu T, Gonul N, Baykara T. Preparation and in
drugs to a specific body site have a vast impact on the
vitro evaluation of modified release ketoprofen
health care system. A microsponge delivery system can
microsponges. ll Farmaco. (2003) 101-6.
release its active ingredient on a time mode and also in
14. Martin A., Swarbrick J., Cammarrata A. In:Physical
response to other stimuli. Therefore, microsponge has got
Pharmacy- Physical Chemical Principles in Pharma-
a lot of potential and is a very emerging field which is
ceutical Sciences. 3rd Ed. (1991) 527
needed to be explored. Microsponges constitute a
significant part by virtue of their small size and efficient
characterization
thermoresponsive
Pharmaceutics. (1995) 237-242.
16. Kilicarslan M, Baykara T. The effect of the
De-Jalon EG, Blanco-Prieto MJ, Ygartua P, Santoyo
drug/polymer ratio on the properties of Verapamil
HCl loaded microspheres. Int. J. Pharm. (2003) 99–
microparticles: quantification of the drug in porcine
skin layers. J Control Release. (2001) 191–7.
17. Hibah Aldawsari1 and Shaimaa M. Badr-Eldin.
Bhimavarapu, Ramesetti RamaDevi,
Microsponges as promising vehicle for drug delivery
and targeting: Preparation, characterization and
,Sowjanya Paparaju. Microsponges: As a Novel
Applications. AJPP (8 May, 2013) 876
Imperative for Drug Delivery System. RJPT: (August
18. Jones D.S., Pearce K.J. Investigation of the effects of
some process variables on microencapsulation of
Orlu M, Cevher E, Araman A. Design and evaluation
propranolol HCl by solvent evaporation method. Int J.
of colon specific drug delivery system containing
Pharm (1995) 99-205.
flubiprofen microsponges. Int J Pharm. (2006)
19. Kawashima Y, Niwa T, Takeuchi H, Hino T, Itoh Y,
Furuyama S. Characterization of polymorphs of
Embil K, Nacht S, The microsponge delivery system
tranilast anhydrate and tranilast monohydrate when
(MDS): A topical delivery system with reduced
crystallized by two
solvent change spherical
crystallization techniques. J. Pharm. Sci. (1991) 472-
Microencapsul, 13, (1996) 575-588.
20. Ford J.L., Timmins P. Pharmaceutical Thermal
Techniques and Applications.
Arunabha.reCENT ADVANCES IN MIROSPONGES DRUG
Horwood Ltd.: Chichester .(1989)
DELIVERY SYSTEM. , IJPSRR: (May – June 2011) 13-
Microspheres for Controlled Drug Delivery. Biol.
Gangadharappa, H.V; vishal Gupta N.; Chandra
Pharm. Bull .(2004) 1717- 1724.
Prasad M., Sara; Shivakumar, H.G. Current trends in
22. Peppas N.A., Analysis of Fickian and non-Fickian
Microsponge drug delivery system.
drug release from polymers. Pharm. Acta Helv. (1985)
N.H palookar,A.S kulkarni, D.J Ingale and R.A patil.
Microsponges as innovative drug delivery system.
23. Hibah Aldawsari1 and Shaimaa M. Badr-Eldin.
IJPSN volume 5. issue 1. (April-june 2012) 1600-
Microsponges as promising vehicle for drug delivery
and targeting: Preparation, characterization and
Saroj Kumar Pradhan: microsponges as the versatile
Applications. AJPP (8 May, 2013) 877
tool for drug delivery system
24. Sato T., Kanke M., Schroeder G., Deluca P. Porous
Hibah Aldawsari1 and Shaimaa M. Badr-Eldin.
biodegradable microspheres for controlled drug
Microsponges as promising vehicle for drug delivery
delivery. Assessment of processing conditions and
and targeting: Preparation, characterization and
solvent removal techniques. Pharm Res. (1988) 21-
Applications. AJPP ( 2013) 875
10. Viral Shaha, Hitesh Jain1, Jethva Krishna1, Pramit
25. Kilicarslan M, Baykara T. The effect of the
Patel. Microsponge drug delivery: A Review. IJRPS
drug/polymer ratio on the properties of Verapamil
HCl loaded microspheres. Int. J. Pharm. (2003) 99–
11. Jelvehgari M, Siahi-Shadbad MR, Azarmi S, Gary P,
Martin, Nokhodchi A: The microsponge delivery
IJDDT, October-December 2014, 4(4), 58-66
Hamid Hussain et al. / Microsponges: An Overview…
26. Draize J.H., Woodard G., Calvery H.O. Methods for
Preparation and characterization. Tropical Journal of
the study of irritation and toxicity of substance es
Pharmaceutical Research, (2010) 67-72
applied topically to the Skin and Mucous Membranes.
33. Mine Orlu, Erdal Cevher, Ahmet Araman Design and
J Pharmacol ExpTher .(1944) 377-389.
evaluation of colon specific drug delivery system
27. Saraf A., Dasani A.,Pathan H., Microsponge drug
containing flurbiprofen microsponges, International
delivery system as an innovation in Cosmetic world A
Journal of Pharmaceutics, (2006) 103–117.
Review. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Education
34. Shaheen S Z, Bolla K, Vasu K & Singara C M A.
and Research, (2012) 2278 – 7496
Antimicrobial activity of the fruit extracts of Coccinia
28. Patel G., Patel J., Use of a Microsponge in Drug
indica. African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 8(24)
Delivery Systems, Pharmaceutical processing, (2008)
35. Park W H, Lee S J and Moon H I. Antimalarial
29. D'souza JI. In-vitro Antibacterial and Skin Irritation
Activity of a New Stilbene Glycoside
Studies of Microsponges of Benzoyl Peroxide. Indian
Parthenocissus tricuspidata in Mice. Antimicrobial
Drugs. (2001) 23.
Agents and Chemotherapy. 52(9) (2008): 3451–3453.
30. Wester R., Patel R., Natch S., Leyden J., Melendres J.,
36. Srivastava R, Pathak K. Microsponges: a futuristic
Maibach H., Controlled release of benzoyl peroxide
approach for oral drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug
from a porous microsphere polymeric system can
Deliv., (2012) 863-878.
reduce topical irritancy, J. Am. Acad. Derm., (1991)
37. Embil VP, OTC external analgesic cream/topical
analgesic anti-inflammatory, counterirritant utilizing
31. John I. D'souza, Jagdish K. Saboji, Suresh G. Killedar,
the microsponge delivery system (MDS) for
Harinath N. More "Design and Evaluation of Benzoyl
controlled release of actives, UK Patent 01010586,
Peroxide Microsponges to Enhance Therapeutic
Treatment", Accepted for
38. Grimee PE, Meraz M, A new microentrapped 4%
presentation in 20th FAPA Congress, Bangkok ,
Thailand ,( Nov30- Dec 3, 2004
hyperpigmentation, 60th Annual meeting of American
32. Jain V., Singh R., Dicyclomine-loaded eudragit based
Academy of Dermatology. (2002) 22-27.
microsponge with potential for colonic delivery
IJDDT, October-December 2014, 4(4), 58-66
Source: http://impactfactor.org/IJDDT/4/IJDDT,Vol4,Issue4,Article1.pdf
ARTICLE 48. CONTROLLED SUBSTANCES IC 35-48-1 Chapter 1. Definitions IC 35-48-1-0.1Application of certain amendments to chapter Sec. 0.1. The addition of section 9.3 of this chapter by P.L.225-2003 applies only to a controlled substance offense underIC 35-48-4 that occurs after June 30, 2003.As added by P.L.220-2011, SEC.627. Amended by P.L.63-2012,SEC.81.
© The Authors Journal compilation © 2009 Biochemical SocietyEssays Biochem. (2009) 46, 95–110; doi:10.1042/BSE0460007 Polyamine analogues targeting epigenetic gene regulation Yi Huang*, Laurence J. Marton†, Patrick M. Woster¶ and Robert A. Casero, Jr*1*The Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center at Johns Hopkins, The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Bunting ◊ Blaustein Cancer Research Building, 1650 Orleans Street, Baltimore, MD 21231, U.S.A., †Progen Pharmaceuticals, Redwood City, CA 94065, U.S.A., and ¶Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Wayne State University, Detroit, MI 48202, U.S.A.




