Treatment and rehabilitation of youth with substance use disorder
Case Study Dr. Tabitha Ndungu
presented to
NACADA on
their 2nd
Conference in
Nairobi, Kenya
Date; 10th - 14th JUNE 2013
Venue: Moi Sports Centre
Kasarani Gymnasium
Theme: " The
Youth and
Drugs: A Call to
Action."
In spite of the damage done by
alcohol/drug abuse or addiction, only
four cents of every spent by the 50 states
is devoted to prevention and treatment
of substance use problems.(Grinfield 2001)
Nor are the various state governments
alone in not addressing the issue of
substance abuse.
Introduction (CONT.)
Nationally, less than one-fifth of the
physicians/medical personnel surveyed
considered themselves prepared to deal with
alcohol-dependent patients, while less than 17
thought they had the skills necessary to deal with
prescription drug abusers (National Center on
Addiction and Substance Abuse at Columbia
University, 2000).
Indeed, at the end of training , most physicians
have a more negative attitude toward patients
with substance use disorders than they did at the
beginning of their graduate training (Renner
Introduction (CONT.)
As a result of this professional pessimism,
physicians tend to "resist being involved in
negotiating a referral and brokering a
consultative recommendation when
alcoholism is the diagnosis". (Westermeyer
An example of the outcome of this neglect is
that fewer than 50% of patients who go to
physicians for alcohol-related problems are
actually asked about their alcohol
use.(Pagano, Graham, Frost-Pineda, & Gold
Introduction (CONT.)
Although the benefits of professional
treatment of alcohol abuse/addiction have
been demonstrated time and again, many
physicians continue to consider alcohol and
illicit drug use problems to virtually
untreatable, and they ignore research
findings suggesting otherwise. (Renner 2004b).
Indeed, "more often than, the physician will
view the addicted patient as challenging at
best and not worthy of customary
compassion" (R. Brown 2006).
Introduction (CONT.)
While postgraduate training programs for
physicians and medical personnel have
devoted instructional time to the
treatment of substance use disorders, the
average amount of time devoted to this
training is about 8 hours.( (Renner 2004b).
most medical personnel are ill-prepared
to work with patients with SUD.
Introduction (CONT.)
Marriage/family therapists also share this lack
or preparation in recognizing and dealing
with SUD. When a substance use problem
within a marriage or family is not uncovered,
therapy proceeds in a haphazard fashion.
Vital clues to a very real illness within the
family are missed, and the attempt at family
or marital therapy is ineffective unless the
addictive disorder is identified and
Introduction (CONT.)
In spite of the obvious relationship between
substance abuse and the various forms of
psychopathology , most clinical psychologists are
not wel prepared to deal with issues involving
substance use or abuse. (Sobel & Sobel 2007, p2).
Fully 74% of the psychologists surveyed admitted
that they had no formal education in the
identification or treatment of the addictions and
rate their graduate school training in the area of
drug addiction as inadequate ( Aanavi, Taube, Ja
& Duran 2000). In a very real sense, mental health
professions have responded to the problem of SUD
with a marked lack of attention or professional
TYPES OF THERAPY
Brief Psychotherapy
Core assessment areas
Pharmacotherapy
Brief Psychotherapy
Core assessment areas
Before proceeding with brief therapy for
substance abuse disorders, a number of
areas should be assessed;
Current use patterns
History of substance abuse
Consequences of substance abuse
(especially external pressures that are
bringing the client into treatment at this
time, such as family or legal pressures)
Brief Psychotherapy
Core assessment areas (cont.)
Coexisting psychiatric disorders Information about major medical problems
and health status
Information about education and
Support mechanisms Client strengths and situational advantages Previous treatment Family history of substance abuse disorders
and psychological disorders
Pharmacotherapy for
Substance Use Disorders
Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT) is a
form of pharmacotherapy and refers to
any treatment for a substance use
disorder that includes a pharmacologic
intervention as part of a comprehensive
substance abuse treatment plan with an
ultimate goal of patient recovery with full
social function.
Nicotine Replacement
NRT works by making it easier to abstain from
tobacco by partially replacing the nicotine
previously obtained from tobacco.[29] There
are at least 3 mechanisms by which NRT
could be effective, as follows:
Reducing general withdrawal symptoms, thus
allowing people to learn to get by without
Reducing the reinforcing effects of tobacco-
delivered nicotine
Nicotine Replacement
Exerting some psychological effects on
mood and attention states
Nicotine replacement medications should
not be viewed as standalone medications
that make people stop smoking;
reassurance and guidance from health
professionals are still critical for helping
patients achieve and sustain abstinence.
Types of NRT
Transdermal nicotine patch
Nicotine nasal spray
Nicotine gum
Nicotine lozenge
Sublingual nicotine tablet
Nicotine inhaler
Nicotine Replacement
(NRT) cont.
The first type is intended for longer-term
use, whereas the other 5 types are used
for acute dosing. With the acute-dosing
products, the amount and timing of
nicotine delivery can be titrated by the
user, allowing the use of these products as
rescue medication for cravings.
Nicotine Replacement
Ongoing craving in a quitter is associated
with acute episodes of more intense
craving (ie, breakthrough craving).
Provoked by situational stimuli, such as
seeing someone smoke or experiencing
emotional upset, such episodes are
associated with a very high risk of relapse.
Nicotine Replacement
(NRT) cont.
Acute NRT approaches may also be used
when a situation is expected to produce
a craving (eg, a demanding meeting,
rush-hour traffic, a long commute, or a
social situation where cigarette smokers
will be present).
Common adverse events that are
common to all NRT products include
dizziness, nausea, and headache.
Research of efficacy of NRT
Piper et al conducted a randomized,
placebo-controlled, double-blind trial of 5
smoking cessation pharmacotherapies.[36]
The study population included 1504 adults
who smoked at least 10 cigarettes daily
for the previous 6 months and were
motivated to quit smoking.
Research of efficacy of
Patients were randomly assigned to 1 of
the following groups: nicotine lozenge,
nicotine patch, sustained-release
bupropion, nicotine patch plus nicotine
lozenge, bupropion plus nicotine lozenge,
Research of efficacy of
All treatment groups had smoking cessation
rates differing from those of the placebo
group, but only the nicotine patch–plus–
nicotine lozenge group showed significantly
higher abstinence rates at 6 months after
quitting in comparison with the placebo
The effects of the nicotine lozenge,
bupropion, and bupropion plus lozenge were
comparable with those reported in previous
Case Study; Work in Progress
The following client consulted me after his
very close cousin died of alcoholism. Mr.
X is a young man of 35 years who still live
with the mother. He has a degree in
engineering from one of the universities in
Kenya. He was devastated after his cousin
died from alcoholism. However, he was
not able to go for rehabilitation due to
lack of finances.
Brief Psychotherapy
We had six sessions trying to see the way
forward.
1st session; Forming a therapeutic alliance
2nd session. Assessment of the level of
motivation.
3rd Session; introduction to NICOTINE
REPLACEMENT THERAPY (NRT)
Brief Psychotherapy &
In this case we used chewing gums for 28
4th Session; planning of homework
assignments as well as alternative
activities to replace time he spent
drinking and smoking.
Brief Psychotherapy &
5th Session; addressing any fears he had
and meeting with the family members to
look for ways to offer support.
6th Session; we terminated the counseling
session but left it open that the client can
always call in case of a problem.
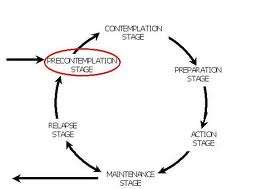
Transtheoretical model ; for brief
psychotherapy , the client MUST be in the
action stage. Mr X was in the action
This is the 7th Month that he has stayed
He left chewing the nicotine gum and has
no craving for tobacco as well as alcohol.
I call it a work in progress as the client is
not two years clean which is the
recommended period to say the client is
clean. He has also gone back to work
and is intending to get married.
Limitation
The case study is still undergoing and other
factors have to be addressed to confirm
whether it is the brief psychotherapy and the
NRT or other factors like employer support,
family support or the guilt of his cousin's
death. It will be good to go beyond and try to
see the benefits combined brief
psychotherapy & pharmacotherapy in drug
addiction management and may be employ
it in our health care system.
Conclusion
No single treatment has been found
adequate but individualized treatment
has been found to benefit more clients.
THANK YOU PLEASE CLAP FOR ME
Source: http://www.nacada.go.ke/documents-and-resources/category/18-treatment-rehabilitation?download=106:theme-4
Bilan des opportunités stratégiques de développement des bio-industries au Québec Évaluation préliminaire des segments d'affaires : Santé humaine Nutrition Biotechnologies © 2007 CQVB. Tous droits réservés. Les présentes sont protégées par la Loi sur le droit d'auteur au Canada et par les traités et conventions internationales en matière de droit d'auteur. Toute reproduction, traduction, adaptation, mémorisation sur un système d'extraction de données, transmission ou autre usage ou divulgation quelconque, en tout ou en partie, et sous quelque sous forme ou par quelque moyen que ce soit, est strictement interdite et nécessite le consentement écrit préalable du CQVB. Les données sont la propriété exclusive du CQVB et ne peuvent non plus être utilisées ou divulguées d'une quelconque façon sans le consentement écrit préalable du CQVB. Ce document devra être retourné sur demande au CQVB.
Reducing Maternal Mortality in Tanzania: Health Facility Assessment in Kigoma Summary Health Facility Assessment of Emergency Obstetric & Neonatal Care Services (EmONC) in Kigoma Region, Tanzania: Selected Findings Tanzania has the fourth highest number of maternal deaths in Sub-Saharan Africa and the sixth highest in the world (World Health Organization, 2014). The

